Teleradiology
Teleradiology is an extension of the radiology service, within which the specialist interprets the pictures made by the radiology department. Many articles have already been published on the technological developments of this service, but little attention has been given to its expected impact on the delivery of health care. This review article will therefore outline the historical and current technological developments of teleradiology services and their potential future implementation into mainstream radiology.
History
Teleradiology services have been practiced for several years within the US and Europe and are currently being introduced in many developing countries. Its elemental objective of it is to produce a quicker, additional correct, and less high-priced difference to ancient medical practices.
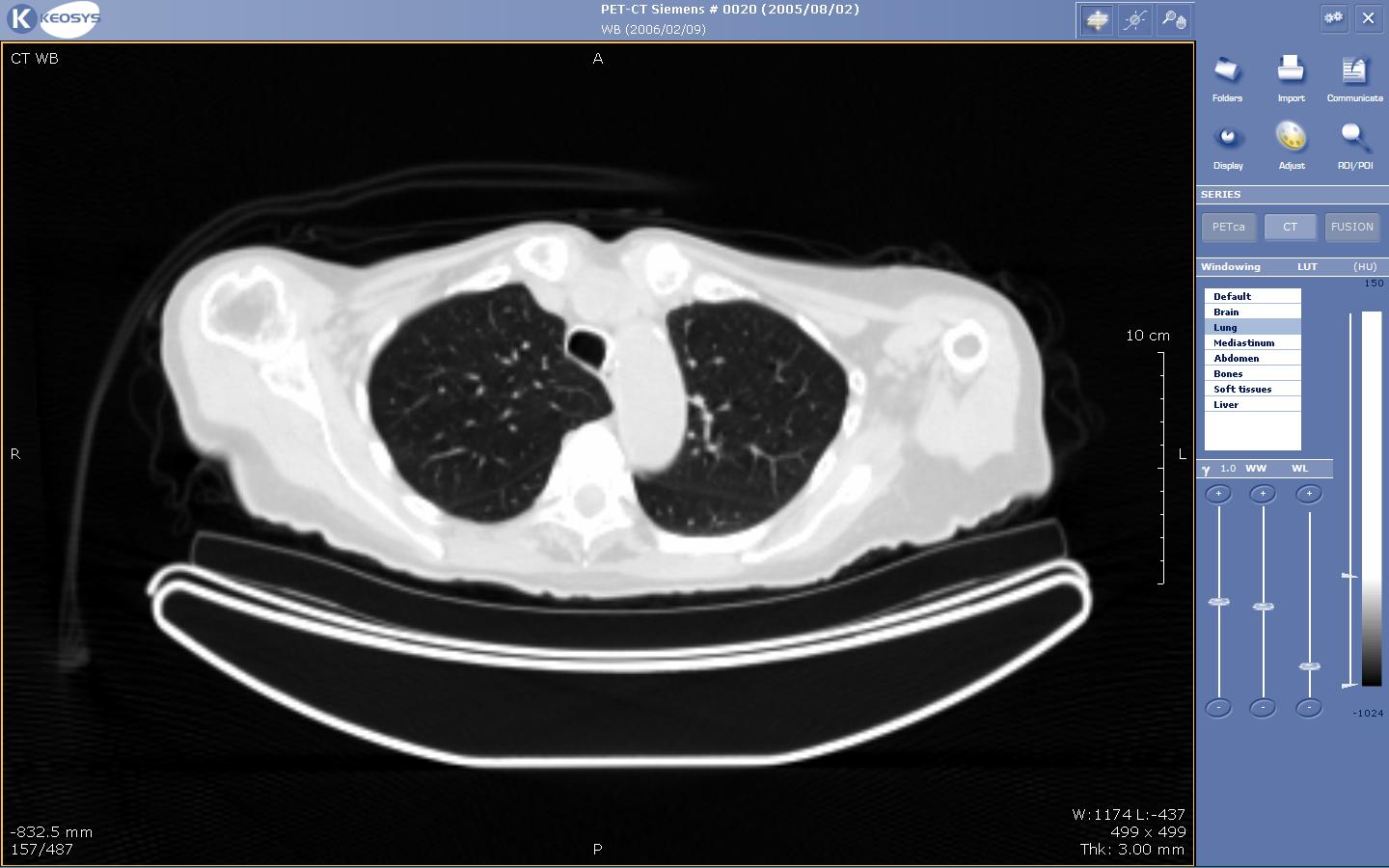
Radiology was supported by a technological discovery by Wilhelm Roentgen in 1895. Teleradiology in addition had its roots in geologic technology chemical analysis back to 1947 with the triumphant transmission of photography footage through phone lines. Diagnostic radiology has become the eye of medication in terms of designation and treating injury and unhealthiness. This text documents the empirical foundations of teleradiology.
The proof concerning the feasibleness of teleradiology and connected data technology applications has been well documented for many decades. The bulk of studies centered on intermediate outcomes, as indicated by equivalence between teleradiology and standard radiology. a homogenous trend of concordance between the 2 modalities was ascertained in terms of diagnostic accuracy and dependableness. extra advantages embrace reductions in patient transfer, rehospitalization, and length of keep.
Top 3 Main Groups Of Teleradiology-

This may be a quickly evolving field that’s being driven by the increasing convenience and use of electronic data and communication technologies. These technologies are incorporated into the look of teleradiology systems, which may be classified into 3 main groups:
1. Remote access teleradiology systems:
The radiology department is physically remote from the patient and the images are viewed on a computer terminal at the remote site.
2. Video-based teleradiology systems:
The images are viewed on a computer monitor at the remote end and transmitted to the radiologist for interpretation.
3. Electronic image transfer (EIT) systems:
The images are transmitted electronically to a computer terminal at the remote end.
Modalities Of Teleradiology –
Today, it’s troublesome to tell apart between regular radiology and teleradiology because the typical advancement, from the angle of the specialist, is extremely identical. All are the same, but for this review, it’s vital to outline and clarify basic terms and components that apply to each kind of practice. In order to understand it better.
The most common form of radiology examination is the X-ray or plain film image. A generator creates a beam of X-rays that’s transmitted through a part of the body into consideration or an organ of interest. X-rays are absorbed by the tissues they have in numerous amounts, counting on tissue density and composition. Bones absorb over soft tissues like muscles. The beams that don’t seem to be absorbed have the body and area unit recorded. Originally, X-rays were recorded on special picture-taking film, however, within the Eighties, digital detectors were developed, resulting in the digital revolution in radiology.
Today, nearly all X-ray pictures are unit non-inheritable exploitation digital detectors and area units displayed on pc monitors instead of writing on film.
Modern teleradiology services had their origins within the development of DR. For over eighty years since the beginning of radiology, patient care trusted film-based capture and future viewing of the pictures on a lightweight box. Film-based pictures had to be transported throughout the hospital, between hospitals, and between varied locations, typically at considerable distances from one another. This technique was effortful, long, inconvenient, and not systematically reliable because of loss or malposition of pictures.
The setup for exchanging all X-ray films into an associated electronic-based imaging system began in earnest within the Seventies. The work grew out of analysis with video-based and different digital detector systems.
Effect Of Coronavirus On Teleradiology Studies-
While it has been around for several years, it hasn’t become widespread as yet, largely as a result of the technology creating it troublesome to do studies of pictures from totally different facilities, each having its own interface and system. However cooperative Imaging has enabled its radiologists to be ready to read studies from any facility.
The quick and pervasive adoption of these services has led to many vital changes on the far side preventing the unfolding of (coronavirus)COVID-19. The network of radiologists extends from the geographic area to Hawaii, which implies the power to investigate pictures in the least hours has extended moreover. Hawaii physicians are within the middle of their workday because the remainder of the country slows down and heads to bed, which means the amount of radiologists obtainable for nighttime studies has conjointly magnified.
Because there’s a whole network of radiologists obtainable to hospitals and physicians, the speed at which the studies are being scanned has conjointly improved. This can be particularly vital because the threat of coronavirus puts totally different regions at risk. If there’s a pandemic in one region of the country that gets rid of a variety of radiologists, healthy physicians in different areas will improve to scan the studies and keep the ability running. “The turnaround from the test to reading the study has gone down dramatically,” Chopra says. “We are able to jump in and read them quickly across the board.”
CONCLUSION. Teleradiology can facilitate inflated imaging efficiency and mitigate geographic and temporal discrepancies in imaging care. Technologic limitations and restrictive hurdles hinder the optimum follower of teleradiology, and future attention to those issues may facilitate broader patient access to high-quality imaging across the North American nation.

