Radiology In A Nutshell: Radiology, often known as diagnostic imaging, is a group of tests that take photos or images of various parts of the body. Many of these tests are one-of-a-kind in that they allow doctors to view the human body. This image can be obtained using a variety of imaging tests, including X-rays, MRIs, ultrasounds, CT scans, and PET scans.
It’s a crucial test that tells doctors what’s wrong and which body parts have been harmed and need to be repaired. It is a crucial test in the detection of cancer. It provides surgeons with a comprehensive picture of the tumor’s size, location, and positioning, allowing them to gently remove it and provide appropriate treatment. Let’s see what is radiology used for-
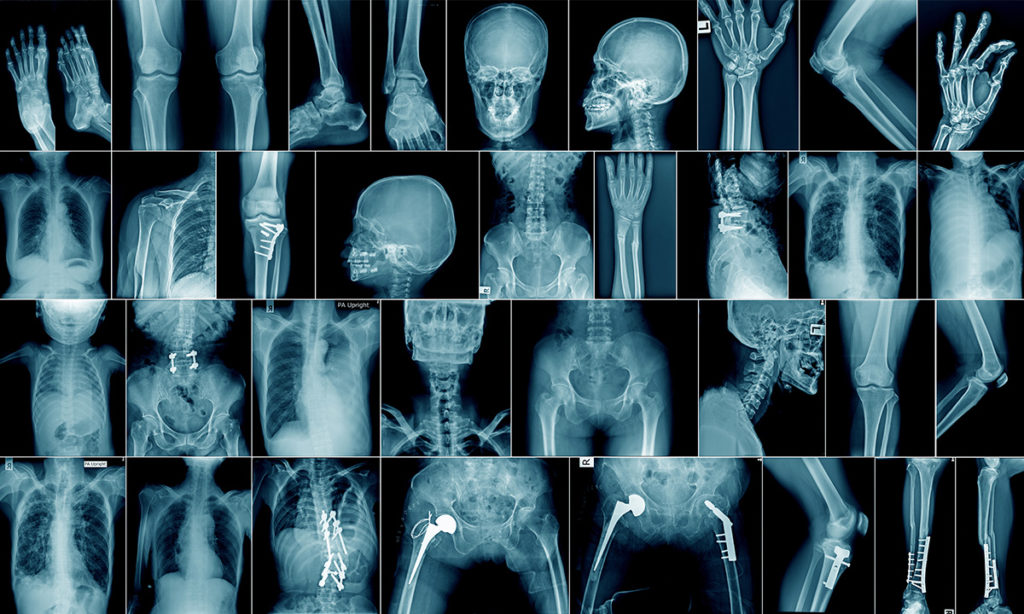
Radiology: A Specialty That Diagnoses And Treats Diseases Using Medical Imaging.
Radiology: A Specialty That Diagnoses And Treats Diseases: Radiology is used to treat a wide range of ailments, and it is classified based on the type of radiology and the imaging test employed. The following are examples of imaging tests:
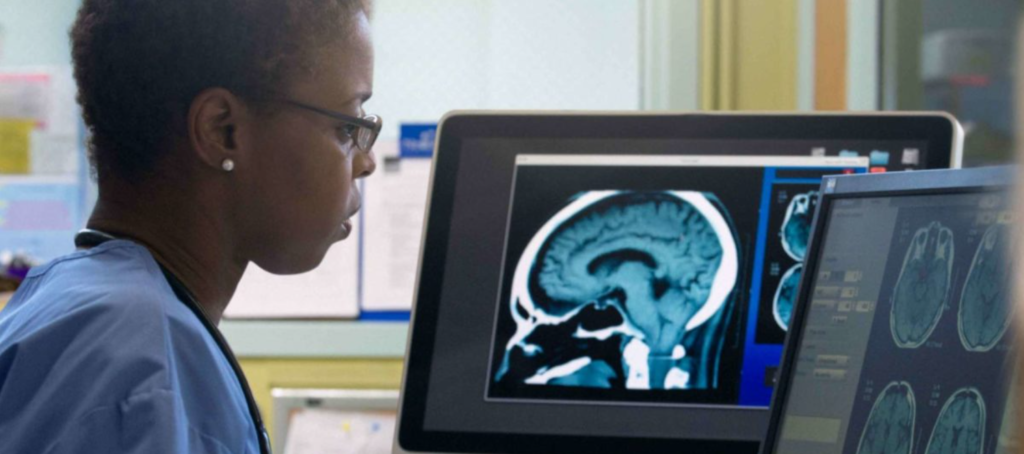
Everything You Should Know About Getting Imaging Tests | A Comprehensive Guide
- Radiographs: X-rays to look at bones, the chest, or the abdomen.
- CT (Computed Tomography): A CT captures multiple x-ray angles of the patient using a doughnut-shaped machine, then creates computer-processed images.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): An MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves with computer processing to create images.
- Mammograms: Specially powered x-rays that look at breast tissues.
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to create moving images that display on a monitor, commonly used for echocardiograms and examining the womb during pregnancy.
- Fluoroscopy: X-rays that make moving images of the body in real time. This imaging is crucial for many procedures, especially those involving the gastrointestinal tract.
- Nuclear medicine: These are short-acting radioactive substances that generate light from bodily processes. A camera collects the light, so a computer can process it and develop an image.
- Diagnostic Radiology– Diagnostic radiology is a medical specialty that entails a variety of imaging procedures to get images of the body’s interior. The diagnostic radiologist next interprets the images to determine the nature of the illness or injury. Diagnostic radiology is at the core of clinical decision-making in modern medicine.
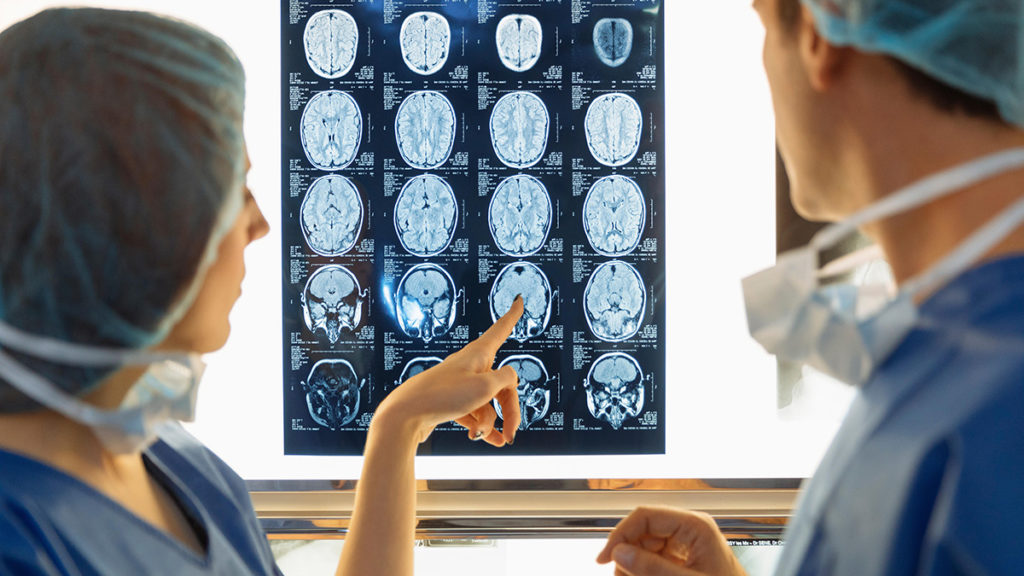
- Interventional Radiology- Interventional radiology is a medical specialty that entails a variety of imaging procedures to get images of the internal organs. These images are carefully interpreted by an interventional radiologist in order to identify injury and disease, as well as to execute a variety of interventional medical procedures. X-rays, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scans, fluoroscopy (an X-ray treatment that allows you to observe inside organs in motion), CT (computed tomography) scans, and ultrasounds are all used by interventional radiologists. Interventional radiologists use tiny instruments and thin plastic tubes (catheters) to do treatments such as treating tumours, obtaining organ biopsies, and installing stents in the body via an artery or vein. The images are utilised to direct the catheters and equipment to the correct location for the procedure or treatment. Treatment can be administered through a little plastic tube about the size of a straw, which eliminates the need for standard (open) or keyhole (laparoscopic) surgery.
- Radiation Oncology- Radiation oncology treats cancer and various non-malignant disorders with radiation (radiation treatment). It is a safe and effective treatment for a variety of diseases, with radiation therapy accounting for 40 percent of all cancer patients cured worldwide.
Radiation therapy- Radiation therapy can be used to treat malignancies throughout the body. It stops cancer cells from growing, proliferating, and spreading by killing or damaging them. Cancerous cells are more vulnerable to the effects of radiation than healthy cells.
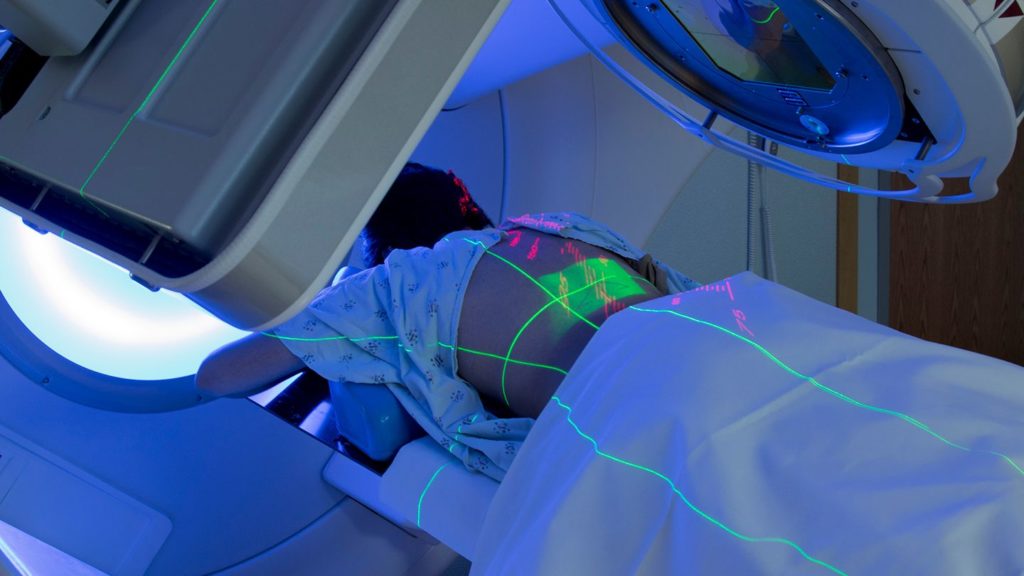
Several types of high-energy radiation are used in treatment, including:
- High energy X-rays
- Electron beams
- Gamma rays.
Diagnostic radiology uses imaging results to identify a wide range of problems, from broken bones to heart conditions and blood clots. Interventional radiology also uses imaging such as CT scans, MRIs,s and ultrasounds to guide medical procedures. Radiation oncology treats cancer using gamma rays and different high-energy radiation. Patients are typically awake during these procedures, whether it’s treating cancer, back pain, or liver and kidney problems. In some cases, interventional radiology eliminates the need for surgery and scopes. Early diagnosis saves lives. Without diagnosis there can be no treatment, there can be no cure.
You May Also Like : Emotion, Memory, and Brain Scans!! Is there really any connection?

